
Hi Everybody:
This week we will be looking at December 2012 -what's happening and some things that could happen. As always, I bring You several points of view from Google You Tube and a fact sheet from Wikipedia. I have created none of this information only the format below. Google has created none of this information, only placed it in the library. I invite You to wake up and view this post with information pertinent to
Dec 21 date (10 days).
Some people our concerned about a old Mayan prediction. It seems some Mayans are concerned about CERN. And the whole world is looking for Higgs Boson. Most people are just sleepy and 'waiting on the World to Change'; hoping 'Gravity' will hold them down on the ground. We will explore these ideas tonight!
http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=U8y0MR8KiY8
flippingmonk
Published on Nov 6, 2012
Ac Tah, of the Mayan people, gave a talk in Santa Monica last month. In this exert he speaks about what is happening around December 21st 2012 and it's significance to the world. His heritage is authentic. Check out his website for lots more information and to see the work Ac Tah and a lot of other dedicated people are doing.... www.actah2012.com
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/CERN
CERN
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
The European Organization for Nuclear Research (French: Organisation européenne pour la recherche nucléaire), known as CERN or Cern ( /ˈsɜrn/; French pronunciation: [sɛʁn]; see History) is an international organization whose purpose is to operate the world's largest particle physics laboratory. Established in 1954, the organization is based in the northwest suburbs of Geneva on the Franco–Swiss border, (46°14′3″N 6°3′19″E) and has 20 European member states.
/ˈsɜrn/; French pronunciation: [sɛʁn]; see History) is an international organization whose purpose is to operate the world's largest particle physics laboratory. Established in 1954, the organization is based in the northwest suburbs of Geneva on the Franco–Swiss border, (46°14′3″N 6°3′19″E) and has 20 European member states.
The term CERN is also used to refer to the laboratory, which employs just under 2,400 full-time employees, 1,500 part-time employees, and hosts some 10,000 visiting scientists and engineers, representing 608 universities and research facilities and 113 nationalities.
CERN's main function is to provide the particle accelerators and other infrastructure needed for high-energy physics research - as a result, numerous experiments have been constructed at CERN following international collaborations. It is also the birthplace of theWorld Wide Web. The main site at Meyrin has a large computer centre containing powerful data-processing facilities, primarily for experimental data analysis; because of the need to make these facilities available to researchers elsewhere, it has historically been a major wide area networking hub.
| European Organization for Nuclear Research Organisation européenne pour la recherche nucléaire | |
|---|---|
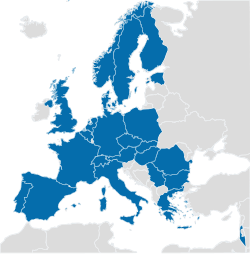 Member states | |
| Formation | 29 September 1954[1] |
| Headquarters | Geneva, Switzerland |
| Membership | 20 member states and 7 observers |
| Director General | Rolf-Dieter Heuer |
| Website | cern.ch |
History
The convention establishing CERN was ratified on 29 September 1954 by 12 countries in Western Europe.[1] The acronym CERN originally stood in French for Conseil Européen pour la Recherche Nucléaire (European Council for Nuclear Research), which was a provisional council for setting up the laboratory, established by 12 European governments in 1952. The acronym was retained for the new laboratory after the provisional council was dissolved, even though the name changed to the current Organisation Européenne pour la Recherche Nucléaire (European Organization for Nuclear Research) in 1954.[2] According toLew Kowarski, a former director of CERN, when the name was changed the acronym could have become the awkward OERN, and Heisenberg said that the acronym could "still be CERN even if the name is [not]".[citation needed]
Soon after its establishment the work at the laboratory went beyond the study of the atomic nucleus into higher-energy physics, which is mainly concerned with the study of interactions between particles. Therefore the laboratory operated by CERN is commonly referred to as the European laboratory for particle physics (Laboratoire européen pour la physique des particules) which better describes the research being performed at CERN.
[edit]Scientific achievements
Several important achievements in particle physics have been made during experiments at CERN. They include:
- 1973: The discovery of neutral currents in the Gargamelle bubble chamber.[3]
- 1983: The discovery of W and Z bosons in the UA1 and UA2 experiments.[4]
- 1989: The determination of the number of light neutrino families at the Large Electron–Positron Collider (LEP) operating on the Z boson peak.
- 1995: The first creation of antihydrogen atoms in the PS210 experiment.[5]
- 1999: The discovery of direct CP violation in the NA48 experiment.[6]
- 2010: The isolation of 38 atoms of antihydrogen[7]
- 2011: Maintaining antihydrogen for over 15 minutes[8]
- 2012: A boson with mass around 125 GeV consistent with long-sought Higgs boson.[9]
The 1984 Nobel Prize in physics was awarded to Carlo Rubbia and Simon van der Meer for the developments that led to the discoveries of the W and Z bosons. The 1992 Nobel Prize in physics was awarded to CERN staff researcher Georges Charpak "for his invention and development of particle detectors, in particular the multiwire proportional chamber."
[edit]Computer science
See also: History of the World Wide Web
The World Wide Web began as a CERN project called ENQUIRE, initiated by Tim Berners-Lee in 1989 and Robert Cailliau in 1990.[10] Berners-Lee and Cailliau were jointly honoured by theAssociation for Computing Machinery in 1995 for their contributions to the development of the World Wide Web.
Based on the concept of hypertext, the project was aimed at facilitating sharing information among researchers. The first website went on-line in 1991. On 30 April 1993, CERN announced that the World Wide Web would be free to anyone. A copy[11] ofthe original first webpage, created by Berners-Lee, is still published on the World Wide Web Consortium's website as a historical document.
Prior to the Web's development, CERN had been a pioneer in the introduction of Internet technology, beginning in the early 1980s. A short history of this period can be found at CERN.ch.[12]
More recently, CERN has become a centre for the development of grid computing, hosting projects including the Enabling Grids for E-sciencE (EGEE) and LHC Computing Grid. It also hosts the CERN Internet Exchange Point (CIXP), one of the two main internet exchange points in Switzerland.
[edit]Faster-than-light neutrino anomaly
Main article: Faster-than-light neutrino anomaly
On 22 September 2011, the OPERA Collaboration reported the detection of 17-GeV and 28-GeV muon neutrinos, sent 730 kilometers (454 miles) from CERN near Geneva, Switzerland to the Gran Sasso National Laboratory in Italy, traveling apparently faster than light by a factor of 2.48×10−5 (approximately 1 in 40,000), a statistic with 6.0-sigma significance.[13] However, in March 2012 it was reported by a new team of scientists for CERN, Icarus, that the previous experiment was most likely flawed and will be retested by scientists of both the Opera and Icarus teams;[14] on 16 March, CERN came up with press release, saying the results were flawed due to incorrectly connected GPS-synchronization cable.[15]
[edit]Particle accelerators
[edit]Current complex
CERN operates a network of six accelerators and a decelerator. Each machine in the chain increases the energy of particle beams before delivering them to experiments or to the next more powerful accelerator. Currently active machines are:
- Two linear accelerators generate low energy particles. Linac2 accelerates protons to 50 MeV for injection into the Proton Synchrotron Booster (PSB), and Linac3 provides heavy ions at 4.2 MeV/u for injection into the Low Energy Ion Ring (LEIR).[16]
- The Proton Synchrotron Booster increases the energy of particles generated by the proton linear accelerator before they are transferred to the other accelerators.
- The Low Energy Ion Ring (LEIR) accelerates the ions from the ion linear accelerator, before transferring them to the Proton Synchrotron (PS). Thisaccelerator was commissioned in 2005, after having been reconfigured from the previousLow Energy Antiproton Ring (LEAR).
- The 28 GeV Proton Synchrotron (PS), built in 1959 and still operating as a feeder to the more powerful SPS.
- The Super Proton Synchrotron (SPS), a circular accelerator with a diameter of 2 kilometres built in a tunnel, which started operation in 1976. It was designed to deliver an energy of 300 GeV and was gradually upgraded to 450 GeV. As well as having its own beamlines for fixed-target experiments (currently COMPASS and NA62), it has been operated as a proton–antiproton collider (the SppS collider), and for accelerating high energy electrons and positrons which were injected into the Large Electron–Positron Collider (LEP). Since 2008, it has been used to inject protons and heavy ions into theLarge Hadron Collider (LHC).
- The On-Line Isotope Mass Separator (ISOLDE), which is used to study unstable nuclei. The radioactive ions are produced by the impact of protons at an energy of 1.0–1.4 GeV from the Proton Synchrotron Booster. It was first commissioned in 1967 and was rebuilt with major upgrades in 1974 and 1992.
- REX-ISOLDE increases the charge states of ions coming from the ISOLDE targets, and accelerates them to a maximum energy of 3 MeV/u.
- The Antiproton Decelerator (AD), which reduces the velocity of antiprotons to about 10% of the speed of light for research intoantimatter.
- The Compact Linear Collider Test Facility, which studies feasibility issues for the future normal conducting linear collider project.
[edit]The Large Hadron Collider
Main article: Large Hadron Collider
Most of the activities at CERN are currently directed towards operating the new Large Hadron Collider (LHC), and the experiments for it. The LHC represents a large-scale, worldwide scientific cooperation project.
The LHC tunnel is located 100 metres underground, in the region between the Geneva International Airport and the nearby Jura mountains. It uses the 27 km circumference circular tunnel previously occupied by LEP which was closed down in November 2000. CERN's existing PS/SPS accelerator complexes will be used to pre-accelerate protons which will then be injected into the LHC.
Seven experiments (CMS, ATLAS, LHCb, MoEDAL[17] TOTEM, LHC-forward and ALICE) will run on the collider; each of them will study particle collisions from a different point of view, and with different technologies. Construction for these experiments required an extraordinary engineering effort. Just as an example, a special crane had to be rented from Belgium in order to lower pieces of the CMS detector into its underground cavern, since each piece weighed nearly 2,000 tons. The first of the approximately 5,000 magnets necessary for construction was lowered down a special shaft at 13:00 GMT on 7 March 2005.
This accelerator has begun to generate vast quantities of data, which CERN streams to laboratories around the world for distributed processing (making use of a specialised grid infrastructure, the LHC Computing Grid). In April 2005, a trial successfully streamed 600 MB/s to seven different sites across the world. If all the data generated by the LHC is to be analysed, then scientists must achieve 1,800 MB/s before 2008.
The initial particle beams were injected into the LHC August 2008.[18] The first attempt to circulate a beam through the entire LHC was at 8:28 GMT on 10 September 2008,[19] but the system failed because of a faulty magnet connection, and it was stopped for repairs on 19 September 2008.
The LHC resumed operation on Friday 20 November 2009 by successfully circulating two beams, each with an energy of 3.5 trillion electron volts. The challenge that the engineers then faced was to try to line up the two beams so that they smashed into each other. This is like "firing two needles across the Atlantic and getting them to hit each other" according to the LHC's main engineer Steve Myers, director for accelerators and technology at the Swiss laboratory.
At 1200 BST on Tuesday 30 March 2010 the LHC successfully smashed two proton particle beams travelling with 3.5 TeV (trillion electron volts) of energy, resulting in a 7 TeV event. However, this is just the start of the road toward the expected discovery of the Higgs boson. This is mainly because the amount of data produced is so huge it could take up to 24 months to completely analyse it. When the 7 TeV experimental period ended, the LHC revved up to 8 TeV (4 TeV acceleration in both directions) in March 2012, and will begin particle collisions at that rate in early April 2012. At the end of 2012 the LHC will be shut down for maintenance for up to two years, to strengthen the huge magnets inside the accelerator. It will then attempt to create 14 TeV events. In July 2012, CERN scientists claimed to have discovered a new sub-atomic particle that could be the much sought after Higgs boson believed to be essential for formation of the Universe.[20]
[edit]Decommissioned accelerators
- The original linear accelerator (LINAC 1).
- The 600 MeV Synchrocyclotron (SC) which started operation in 1957 and was shut down in 1991.
- The Intersecting Storage Rings (ISR), an early collider built from 1966 to 1971 and operated until 1984.
- The Large Electron–Positron Collider (LEP), which operated from 1989 to 2000 and was the largest machine of its kind, housed in a 27 km-long circular tunnel which now houses the Large Hadron Collider.
- The Low Energy Antiproton Ring (LEAR), commissioned in 1982, which assembled the first pieces of true antimatter, in 1995, consisting of nine atoms of antihydrogen. It was closed in 1996, and superseded by the Antiproton Decelerator.
Sites
The smaller accelerators are on the main Meyrinsite (also known as the West Area), which was originally built in Switzerland alongside the French border, but has been extended to span the border since 1965. The French side is under Swiss jurisdiction and there is no obvious border within the site, apart from a line of marker stones. There are six entrances to the Meyrin site:[citation needed]
- A, in Switzerland, for all CERN personnel at specific times.
- B, in Switzerland, for all CERN personnel at all times. Often referred to as the main entrance.
- C, in Switzerland, for all CERN personnel at specific times.
- D, in Switzerland, for goods reception at specific times.
- E, in France, for French-resident CERN personnel at specific times. Controlled by customs personnel. Named "Porte Charles de Gaulle" in recognition of his role in the creation of CERN.[21]
- Tunnel entrance, in France, for equipment transfer to and from CERN sites in France by personnel with a specific permit. This is the only permitted route for such transfers. Under the CERN treaty, no taxes are payable when such transfers are made. Controlled by customs personnel.
The SPS and LEP/LHC tunnels are almost entirely outside the main site, and are mostly buried under French farmland and invisible from the surface. However they have surface sites at various points around them, either as the location of buildings associated with experiments or other facilities needed to operate the colliders such as cryogenic plants and access shafts. The experiments are located at the same underground level as the tunnels at these sites.
Three of these experimental sites are in France, with ATLAS in Switzerland, although some of the ancillary cryogenic and access sites are in Switzerland. The largest of the experimental sites is the Prévessin site, also known as the North Area, which is the target station for non-collider experiments on the SPS accelerator. Other sites are the ones which were used for the UA1, UA2 and the LEP experiments (the latter which will be used for LHC experiments).
Outside of the LEP and LHC experiments, most are officially named and numbered after the site where they were located. For example,NA32 was an experiment looking at the production of charmed particles and located at the Prévessin (North Area) site while WA22 used the Big European Bubble Chamber (BEBC) at the Meyrin (West Area) site to examine neutrino interactions. The UA1 and UA2experiments were considered to be in the Underground Area, i.e. situated underground at sites on the SPS accelerator.
Most of the roads on the CERN campus are named after famous phycisists, e.g.- Richard Feynman, Niels Bohr, Albert Einstein.
[edit]Participation and Funding
[edit]Member states and Budget
Since its foundation by 12 members in 1954, CERN regularly accepted new members. All new members have remained in the organisation continuously since their accession, except Spain and Yugoslavia. Spain first joined CERN in 1961, withdrew in 1969, and rejoined in 1983. Yugoslavia was a founding member of CERN but left in 1961. Initially only West Germany was a (founding) member of CERN. Of the twenty members, 18 are European Union member states. Switzerland and Norway are not.
| Member state | Status since | Contr. (mill.CHFfor 2012) | Contr. (% for 2012) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 29 September 1954 | 30.83 | 2.62% | |
| 29 September 1954 | 19.86 | 1.69% | |
| 29 September 1954 | 169.82 | 14.46% | |
| 29 September 1954 | 219.10 | 18.65% | |
| 29 September 1954 | 120.62 | 10.27% | |
| 29 September 1954 | 49.71 | 4.23% | |
| 29 September 1954 | 26.85 | 2.29% | |
| 29 September 1954 | 29.81 | 2.54% | |
| 29 September 1954 | 55.70 | 4.74% | |
| 29 September 1954 | 146.96 | 12.51% | |
| 1 June 1959 | 23.70 | 2.02% | |
| 11 March 1999 | 3.08 | 0.26% | |
| 1 July 1993 | 10.60 | 0.90% | |
| 1 January 1991 | 15.01 | 1.28% | |
| 29 September 1954 | 17.75 | 1.51% | |
| 1 July 1992 | 6.85 | 0.58% | |
| 1 January 1986 | 14.49 | 1.23% | |
| 1 July 1991 | 31.36 | 2.67% | |
| 1 July 1993 | 5.20 | 0.44% | |
| 1 January 1983 | 87.73 | 7.47% | |
| Candidate, Associate Members | |||
| 2008 | 5.02 | 0.43% | |
| 2011 | 3.63 | 0.31% | |
| 2012 | % | ||
| 2012[25] | % | ||
| Total Members, Candidates and Associates | 1,092.68[26] | 93.01% | |
| 1 July 1985[28] | 17.3 | 1.47% | |
| Other income | — | 64.8 | 5.52% |
| Total CERN | 1,174.78[27] | 100.0% |
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j 12 founding members drafted the Convention for the Establishment of a European Organization for Nuclear Researchwhich entered into force on 29 September 1954.[22][23]
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j Acceded members became CERN member states upon signing an accession agreement.[24]
- ^ a b c d Additional contribution from Candidates for Accession and Associate Member States.[24]
| [show]Maps of the history of CERN membership |
|---|
[edit]Enlargement
Associate Members, Candidates (note that dates are initial signature, not of ratification):
 Romania became a candidate for accession to CERN in 2010 and will become a member in 2015.[29]
Romania became a candidate for accession to CERN in 2010 and will become a member in 2015.[29] Serbia became a candidate for accession to CERN on 19 December 2011, associate member on 10 January 2012.[30]
Serbia became a candidate for accession to CERN on 19 December 2011, associate member on 10 January 2012.[30] Israel became an associate member in 2011, with a decision to be made on its full membership in 2013.[31]
Israel became an associate member in 2011, with a decision to be made on its full membership in 2013.[31] Cyprus became an associate member in 2012.[32]
Cyprus became an associate member in 2012.[32]
Four countries applying for membership have all formally confirmed their wish to become members.[33]
 Slovenia since 7 January 1991, Non-Member State status
Slovenia since 7 January 1991, Non-Member State status Turkey since 1961, Observer State status
Turkey since 1961, Observer State status
[edit]International relations
Five countries have observer status:[34]
 Turkey – since 1961
Turkey – since 1961 Russia – since 1993
Russia – since 1993 Japan – since 1995
Japan – since 1995 United States – since 1997
United States – since 1997 India – since 2002
India – since 2002
Also observers are the following international organizations:
 UNESCO – since 1954
UNESCO – since 1954 European Commission – since 1985
European Commission – since 1985
Non-Member States (with dates of Co-operation Agreements) currently involved in CERN programmes are:
 Algeria
Algeria Argentina – 11 March 1992
Argentina – 11 March 1992 Armenia – 25 March 1994
Armenia – 25 March 1994 Australia – 1 November 1991
Australia – 1 November 1991 Azerbaijan – 3 December 1997
Azerbaijan – 3 December 1997 Belarus – 28 June 1994
Belarus – 28 June 1994 Brazil – 19 February 1990 & October 2006
Brazil – 19 February 1990 & October 2006 Canada – 11 October 1996
Canada – 11 October 1996 Chile – 10 October 1991
Chile – 10 October 1991 China – 12 July 1991, 14 August 1997 & 17 February 2004
China – 12 July 1991, 14 August 1997 & 17 February 2004 Colombia – 15 May 1993
Colombia – 15 May 1993 Croatia – 18 July 1991
Croatia – 18 July 1991 Cuba
Cuba Cyprus – 14 February 2006
Cyprus – 14 February 2006 Egypt – 16 January 2006
Egypt – 16 January 2006 Estonia – 23 April 1996
Estonia – 23 April 1996 Georgia – 11 October 1996
Georgia – 11 October 1996 Iceland – 11 September 1996
Iceland – 11 September 1996 Iran – 5 July 2001
Iran – 5 July 2001 Ireland
Ireland Jordan - 12 June 2003.[35] MoU with Jordan and SESAME, in preparation of a cooperation agreement signed in 2004.[36]
Jordan - 12 June 2003.[35] MoU with Jordan and SESAME, in preparation of a cooperation agreement signed in 2004.[36] Lithuania – 9 November 2004
Lithuania – 9 November 2004 Macedonia – 27 April 2009[37]
Macedonia – 27 April 2009[37] Mexico – 20 February 1998
Mexico – 20 February 1998 Montenegro – 12 October 1990
Montenegro – 12 October 1990 Morocco – 14 April 1997
Morocco – 14 April 1997 New Zealand – 4 December 2003
New Zealand – 4 December 2003 Pakistan – 1 November 1994.
Pakistan – 1 November 1994. Peru – 23 February 1993
Peru – 23 February 1993 Romania – 1 October 1991. Since 12 December 2008 it has the Status of Candidate for Accession to Membership.
Romania – 1 October 1991. Since 12 December 2008 it has the Status of Candidate for Accession to Membership. Saudi Arabia – 21 January 2006
Saudi Arabia – 21 January 2006 Slovenia – 7 January 1991
Slovenia – 7 January 1991 South Africa – 4 July 1992
South Africa – 4 July 1992 South Korea – 25 October 2006.
South Korea – 25 October 2006. Republic of China (Taiwan)
Republic of China (Taiwan) Thailand
Thailand United Arab Emirates – 18 January 2006
United Arab Emirates – 18 January 2006 Ukraine – 2 April 1993
Ukraine – 2 April 1993 Vietnam
Vietnam
[edit]Public exhibits
Facilities at CERN open to the public include:
- The Globe of Science and Innovation, which opened in late 2005 and is used four times a week for special exhibits.
- The Microcosm museum on particle physics and CERN history.
- The Hindu deity, Shiva, a 2 metre statue styled on Chola bronzes of the deity engaging in the Nataraja dance of Chidambaram, parallelling the movements or “dance” of subatomic particles.
+++++++++++++++++++++++
VIDEO LINEUP: Learning Tonight!
Published on Oct 17, 2012
For a report on ABC's Catalyst program (http://www.abc.net.au/catalyst/), I visited the Large Hadron Collider in Switzerland to find out what is being done now that the Higgs Boson has been discovered.
Although its mass has been measured around 125-126 GeV most of the other properties of the particle remain unknown. Its spin appears to be 0 or 2 but more results are required to nail this down. If it is the standard model Higgs, the spin should be 0, resulting in a fairly symmetric distribution of decay products in the detectors.
We may know this year if it's not the standard model Higgs - this would be the case if it doesn't decay into specific particles with the expected frequency. However if it is the standard model Higgs, it may take many more years to be certain. The large hadron collider will be shut down in 2013 for upgrades so that higher energies up to 14 TeV can be tested. Right now the LHC is operating at 8 TeV. The next announcement is expected in December.
Although its mass has been measured around 125-126 GeV most of the other properties of the particle remain unknown. Its spin appears to be 0 or 2 but more results are required to nail this down. If it is the standard model Higgs, the spin should be 0, resulting in a fairly symmetric distribution of decay products in the detectors.
We may know this year if it's not the standard model Higgs - this would be the case if it doesn't decay into specific particles with the expected frequency. However if it is the standard model Higgs, it may take many more years to be certain. The large hadron collider will be shut down in 2013 for upgrades so that higher energies up to 14 TeV can be tested. Right now the LHC is operating at 8 TeV. The next announcement is expected in December.
http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=-A-IguX0dRY
http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=bDzdxUrYC6c
Published on Dec 9, 2012
Sorry I meant photons colliding at the speed of light!
What To Expect On December 21st 2012. VR: Tatoott1009 CERN Hidden Date - FOUND, You Decide ! by Montagraph
http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=bDzdxUrYC6c&feature=youtu.be
http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=izwJydaAltw&lc=_vqclJJvKnVv6I707V6k5iXfyy7...
Thanx to Montagraph for his in-depth research into all this. These are the links which he left in his description box if you want to look into it for yourself
Join my facebook group and drop links in the comments concerning the police state
http://www.facebook.com/BarbarianRebellionRadio
What To Expect On December 21st 2012. VR: Tatoott1009 CERN Hidden Date - FOUND, You Decide ! by Montagraph
http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=bDzdxUrYC6c&feature=youtu.be
http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=izwJydaAltw&lc=_vqclJJvKnVv6I707V6k5iXfyy7...
Thanx to Montagraph for his in-depth research into all this. These are the links which he left in his description box if you want to look into it for yourself
Join my facebook group and drop links in the comments concerning the police state
http://www.facebook.com/BarbarianRebellionRadio
Category
License
Standard YouTube License
Published on Dec 4, 2012
Some of the stanege and extreme weather events of this week from floods, bloody beaches, typhoons, massive sinkholes and tornadoes. For more on ufos end times events or strange and extreme weather go to or subscribe to my channel. Thanks for watching and be safe during these strange and extreme times.
Music
Full credit to SteveMusicComposer Stedman for allowing me to use this epic track.
Orchestral Epic Dramatic Sad Symphony Music FiIm score
Find it here
http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=YQ2rOqdD-HU
Other Parts To This Series
Signs Of Change Days After Tomorrow Extreme November Events
http://youtu.be/zO1ZIicc39c
Signs Of Change The Past Week Or So Until
Until November 27 2012
http://youtu.be/6oDoOyPYZFI
Until November 19 2012
http://youtu.be/kR2Q0h-pFzQ
November 12
http://youtu.be/I4FPTqa5JWE
November 7 2012
http://youtu.be/yLlmHG0WVrE
November 2 2012
http://youtu.be/zGgcaDPnv_8
October 26
http://youtu.be/6T1ndxwNz9k
Until October 22
http://youtu.be/bCwBEClZXTw
Until October 15
http://youtu.be/A5a6rmwcVZx
Until October 7
http://youtu.be/A-Shhx8wIbA
Signs Of Change - Earth Pouding Experience
http://youtu.be/2P8-5XJvbOU
Signs Of Change - Insidious Earth
lhttp://youtu.be/Naletci56AI
Signs Of Change - Super Massive Destuction - September 2012
http://youtu.be/_6ZnkjAc8OM
Other great channels
http://youtube.com/user/trulif3r
Check out the series called "Watchers" here
http://www.youtube.com/user/RevelationMediaCo
Earthquake Updates
http://www.youtube.com/user/MegaFighter1981
Find my monthly videos on my other channel. This is also a backup channel.
http://youtube.com/user/GlobalDisaster2013
Music
Full credit to SteveMusicComposer Stedman for allowing me to use this epic track.
Orchestral Epic Dramatic Sad Symphony Music FiIm score
Find it here
http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=YQ2rOqdD-HU
Other Parts To This Series
Signs Of Change Days After Tomorrow Extreme November Events
http://youtu.be/zO1ZIicc39c
Signs Of Change The Past Week Or So Until
Until November 27 2012
http://youtu.be/6oDoOyPYZFI
Until November 19 2012
http://youtu.be/kR2Q0h-pFzQ
November 12
http://youtu.be/I4FPTqa5JWE
November 7 2012
http://youtu.be/yLlmHG0WVrE
November 2 2012
http://youtu.be/zGgcaDPnv_8
October 26
http://youtu.be/6T1ndxwNz9k
Until October 22
http://youtu.be/bCwBEClZXTw
Until October 15
http://youtu.be/A5a6rmwcVZx
Until October 7
http://youtu.be/A-Shhx8wIbA
Signs Of Change - Earth Pouding Experience
http://youtu.be/2P8-5XJvbOU
Signs Of Change - Insidious Earth
lhttp://youtu.be/Naletci56AI
Signs Of Change - Super Massive Destuction - September 2012
http://youtu.be/_6ZnkjAc8OM
Other great channels
http://youtube.com/user/trulif3r
Check out the series called "Watchers" here
http://www.youtube.com/user/RevelationMediaCo
Earthquake Updates
http://www.youtube.com/user/MegaFighter1981
Find my monthly videos on my other channel. This is also a backup channel.
http://youtube.com/user/GlobalDisaster2013
Category
License
Standard YouTube License
http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=UfPnjVMEHfg
Published on Aug 22, 2012
I
http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=9Uh5mTxRQcg
II
http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ASRpIym_jFM
III
http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=6guXMfg88Z8
There You go! I hope the vids give You a starting point on your own personal research for your own personal self! Your odds are 50/50 that something will happen on December 21.
...this is brendasue signing off from Rainbow Creek. See You next time.
Love to All.
Of Course, on more great performance
http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=oBIxScJ5rlY
Uploaded on Oct 3, 2009
Music video by John Mayer performing Waiting On The World To Change. (C) 2006 AWARE RECORDS LLC
Category
License
Standard YouTube License
http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=TErQbwHHh_w
Uploaded on Feb 1, 2009
From the Where The Light Is DVD, John Mayer @ the
Nokia Theatre live in Los Angeles,"Gravity".
Thanks for viewing!
John Mayer - Gravity
Nokia Theatre live in Los Angeles,"Gravity".
Thanks for viewing!
John Mayer - Gravity
Gravity
Is working against me
And gravity
Wants to bring me down
Whoa I'll never know
What makes this man
With all the love
That his heart can stand
Dream of ways
To throw it all away
Whoa Gravity
Is working against me
And gravity
Wants to bring me down
Oh twice as much
Aint twice as good
And can't sustain
Like one half could
It's wanting more
It's gonna send me to my knees
Oh gravity
Stay the hell away from me
Oh gravity
Has taken better men than me
Now how can that be?
Just keep me where the light is
Just keep me where the light is
Just keep me where the light is
Cmon keep me where the light is
Cmon keep me where the light is
Cmon keep me where keep me where the light is
Is working against me
And gravity
Wants to bring me down
Whoa I'll never know
What makes this man
With all the love
That his heart can stand
Dream of ways
To throw it all away
Whoa Gravity
Is working against me
And gravity
Wants to bring me down
Oh twice as much
Aint twice as good
And can't sustain
Like one half could
It's wanting more
It's gonna send me to my knees
Oh gravity
Stay the hell away from me
Oh gravity
Has taken better men than me
Now how can that be?
Just keep me where the light is
Just keep me where the light is
Just keep me where the light is
Cmon keep me where the light is
Cmon keep me where the light is
Cmon keep me where keep me where the light is
Category
License
Standard YouTube License

http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/File:Construction_of_LHC_at_CERN.jpg
O+O












No comments:
Post a Comment
Hi Everybody! Please say hello and follow so I know you are here! Due to the inconsideration of people trying to put commercials on my blog comment area, I have restricted use of anonymous posts. Sorry that some hurt all.
My public email is katescabin@gmail.com No spammers or trolls